Determination of the Density Value with a Densitometer
The density values are measured in this case with "real", that is physical, color filters for red, green and blue or with a visual filter.
Achromatic colors like black are measured with the visual filter. Chromatic colors like CMY are measured with the color filter of the color that is absorbed the most.
See the diagram below for an example:
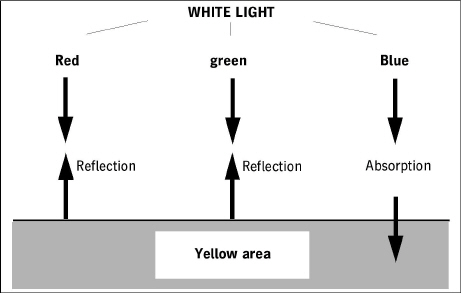
A yellow area absorbs blue light in most cases, red and green are mainly reflected. The more blue is absorbed, that means the less blue is reflected, the greater the density value for yellow. Blue reflection is measured with a blue filter that is transparent only for blue.
Based on this, the following applies for cyan, magenta and yellow:
•Cyan: blue + green reflected / red absorbed
=> measure with the red filter
•Magenta: blue + red reflected / green absorbed => measure with the green filter
•Yellow: red + green reflected / blue absorbed
=> measure with the blue filter
Simplified view: Reflection/absorption for yellow

The following is valid for all chromatic colors, in other words CMY, and also chromatic spot colors: measure using the color filter that determines the maximum density values.
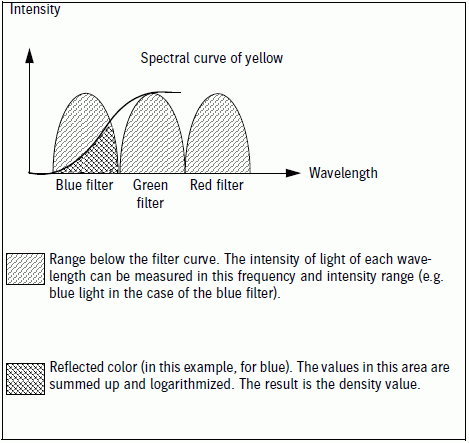
The diagram below shows the spectrum of a yellow hue. The blue filter curve lies in the range in which yellow has the greatest absorption (least intensity). Consequently, yellow is measured with this filter.
Schematic diagram of the RGB filter curves (no real filter curves!)
Nature of the color filter => density status / polarization filter
The curves for the RGB color filters (see above) can be different. In other words, the frequency range in which, for example, the blue filter is transparent for blue light and the intensity values vary.
The density status defines the shape of the color filter curve. The density status states how the density value is derived from the measured light. This is based on ISO standard 5-3.
A density value that was determined only provides you with information if its density status is known and also if a polarization filter was used when measuring the data.
This means that the information about the density status and polarization filter must also be conveyed along with the density value.
The following is valid for all colors:
The density of paper white is subtracted from the measured solid density. Paper white is not to be an influencing factor when determining the density values of the colors.