
Color calculator > Calculate color values

Reference profile
The color calculator can only be used for press profiles. You must open a press profile to view source and target color values. For CMYK, you can use the standard profile set by default, "ISOcoated_v2_eci.icc", in most cases.
Click "Open..." to open the profile browser where you can select and open a press profile.
Note: The profile browser shows details about the process properties if these process parameters are also saved in the ICC press profile.
In the "Profile Browser Configuration" dialog, you can define which parameters you want displayed and in what order.
If you select a Multicolor profile as a reference profile, you can check how a better result can be had in a 5c, 6c or 7c replacement.
Rendering intent defines the approach taken in color reproduction. The target value can be calculated for four different rendering intents:
•Perceptual: reproduction is based on perception or is photographic (separations). In this variant, the colors you wish to reproduce are mapped to the color gamut of the reproduction process (gamut mapping) so that there is no loss of definition in the image when it is reproduced. Normally, the very chromatic colors are desaturated slightly and a pure (neutral) white is reproduced on the white of the medium (for example, of the paper).
•Relative colorimetric: color matched to the medium through lightness and color cast. All colors that cannot be displayed as a result of these measures are located along the outer edges of this gamut and lose some of their definition.
•Saturation: widely used option for reproducing chroma in colors, with less importance attached to retaining lightness. This method is not really suitable for traditional color reproduction but rather for synthetically produced images such as business graphics. Now and again, the "Saturation" intent is implemented in profiles in such a way that you obtain the same results as with "Perceptual".
•Absolute colorimetric: refers to colorimetrically accurate reproductions. This is particularly important for proofs or soft proofs. All colors that are in the displayable range of the process are reproduced without any colorimetric changes. However, to obtain this result, all non-displayable colors must be confined to the outer edges of the gamut, and as a result, a greater loss of definition can occur here in this restricted color gamut than with "Relative Colorimetric".
Note: To evaluate a spot color, "Rendering Intent" must be set to "Absolute colorimetric". This is automatically set with "Import from measured data"; you may have to set it yourself for other modes.
Table
You can select a PANTONE® or HKS color palette in this list box. The names of all colors in this palette are then show in the "Name" box. Select "manually" to enter your own color values. In this case, the "Name" box is disabled.
Select a color from the currently selected palette in this list box.
Some of the spot color tables listed above have very different structures. For example, PANTONE® solid is sorted by numbers whereas PANTONE® PLUS is sorted by saturation. You can simply type in the color number or part of the color name into the box instead of looking for the color in the (long) list. The color calculator automatically shows a matching color from the list.
If your input is not clear, the color calculator proceeds as follows in its search:
1.Items that start with the number or name you entered
2.Items that end with the number or name you entered
3.Items that contain the number or part of the name you entered
Only the first item displays if the search result is ambiguous, in other words if several items matching the search criterion were found. You can go to the other items using the left or right arrow keys on your keyboard. To start a new search, click the list box again and type in a new string.
Input
As a source value, type any Lab, XYZ or LCH value (from existing color samples or known color data).
The values are automatically converted when you switch over the model in the popup menu.
When color data are imported from a color data file, the data are copied directly to the input boxes.
Output
The target value is then calculated for the source value using the loaded profile. The CMYK value and the ΔE deviation to the reference profile that display depend on the profile that was selected.
"S1" thru "S4" refer to the spot color channels. These boxes are enabled only if a multicolor profile (Multicolor option) is open. These display the additional colors.
If the names of the colors are known, they appear as a tooltip when you point the mouse pointer at the initial letter.
Changes
The color box on the very right shows you a preview of the two colors, giving you a first impression of the difference between the target and measured values (displayed on the monitor using a fixed sRGB profile; original value on the top, calculated value on the bottom). All the analysis values are listed below "Changes" to the left of the box.
The accuracy that is possible for the reproduction of the source value is calculated for the print process set by means of the profile and shown as color difference values (color distance) ΔEab or ΔE00 (2000), ΔL, Δa and Δb, ΔH (hue distance) and ΔC (chroma distance).
The value for ΔE00 is particularly important for evaluation of a spot color because this value describes the color deviation in saturated colors more accurately than ΔEab. Values of ΔE00 < 1 show that the spot color is within the color gamut of the process or very close to it and can be replaced satisfactorily by CMYK.
The greater the ΔE00 values, the harder it is to replace the spot color, in other words, color deviation would be all the more noticeable.
With ΔE00 > 1 it is possible to replace the color without any problems; in most cases this is also applicable for ΔE00 between 1 and 2. With ΔE00 > 3 you must decide in the field whether the deviation is still tolerable, with ΔE00 > 6, however, it is only possible to replace the color with Multicolor.
Note: The color difference values calculated are specified as ΔEab as well as the newer ΔE00 (2000). ΔEab is the current definition for calculation of color distance based on the ISO standard of 1976. The more recent formula, ΔE 00, is significantly more complex and produces more accurate values. ΔE00 is more suited than ΔEab especially when replacing spot colors.
Import from measured data
The color data of the selected patch in an open measurement file are copied to the input boxes when you click this button, for example, to compare a spot color you just measured with the color table.
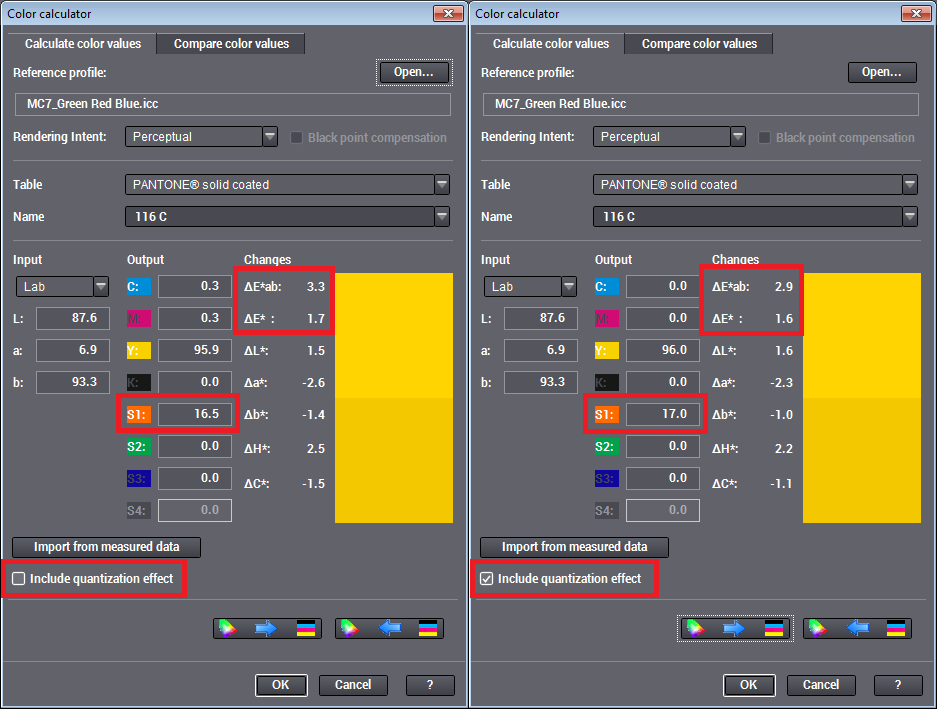
Include quantization effect
The ΔE values are calculated from the comparison of the original CIELab values with the result of the internal conversion of CIELab to CMYK and the transformation of CMYK back to CIELab. Normally, these values are calculated with the highest level of accuracy possible but which cannot be achieved in real conditions.
Example showing quantization effect excluded/included for a 7c multicolor profile and a Pantone spot color:
Calculation

Click the "Lab to CMYK" button to convert the input color value (Lab, XYZ or LCH) to the output tonal value (CMYK and, if necessary, S1, S2, S3).
Note: You must start conversion only if you enter the values manually. Conversion runs automatically when data are imported or taken from the color table.

Click the "CMYK to Lab" button to convert CMYK and, if necessary, S1, S2, S3 to Lab, XYZ or LCH.