RFM analysis - How are our customers grouped in RFM analysis?
(Change language of this page to: English, Deutsch)
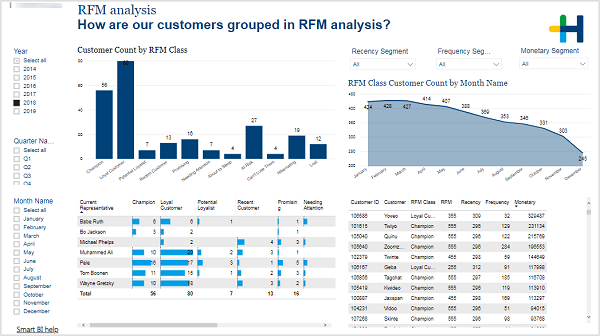
This page can assist you in making decisions based on different customer categories. The customers are categorized by recency, frequency and monetary aspects.

RFM analysis uses three different variables to determine the category a customers belongs to.
•Recency (R): How many days ago did the customer place their last order?
•Frequency (F): How many orders did the customer make in the last 12 months?
•Monetary (M): What is the value of the orders of the last 12 months?
Each customer gets a value from 1 to 5 for each of these variables, with 1 being not good, 5 being good.
|
RFM Class |
R |
F |
M |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Champion (Champion) |
45 |
45 |
45 |
Bought recently, buys often and spends most! |
|
Loyal Customer (Loyal Customer) |
2345 |
345 |
12345 |
Spends often good money. |
|
Potential Loyalist (Potential Loyalist) |
345 |
12345 |
345 |
Recent customers, and spent a good amount. |
|
Recent Customer (Recent Customer) |
345 |
12 |
12 |
Bought most recently, but not often. |
|
Promising (Promising) |
23 |
12 |
12 |
Bought recently, but didn't spend much. |
|
Needing attention (Needing attention) |
23 |
12 |
23 |
Above average recency, frequency and monetary value, but not superb. |
|
About to Sleep (About to Sleep) |
12 |
2345 |
2345 |
Below average recency, frequency and monetary value. |
|
At Risk (1) (At Risk (1)) |
12 |
1 |
345 |
Spent big money, but haven't been seen for a long time. |
|
At Risk (2) (At Risk (2)) |
1 |
345 |
1 |
Bought a lot, but haven't been seen for a long time. |
|
Can’t Lose Them (Can’t Lose Them) |
12 |
12 |
12 |
Keeps ordering small amounts only some times per year. |
|
Hibernating (Hibernating) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
Last order was long time ago, for a small value and only some orders. |
|
Lost (no data) (Lost (no data)) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
No data available for the last 12 months. |
HD Privacy Statement | Imprint | Prinect Know How