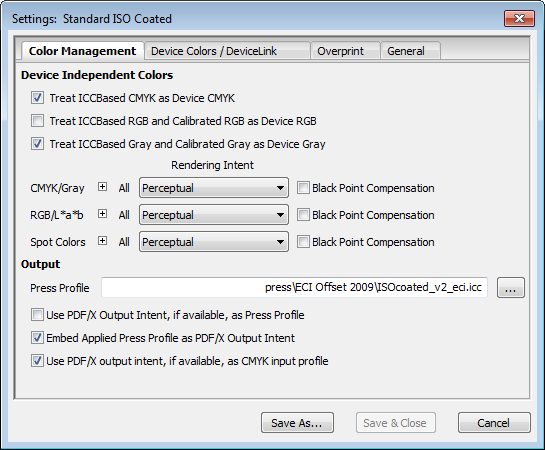
You can define your settings for color matching in this section.

"Device Independent Colors" means that ICC profiles are assigned to the colors of images or graphics. These profiles enable the images or graphics in the original color space (e.g. of a scanner) to be converted without any difficulty to the device-independent Lab color space. The "Lab", "CalibratedRGB" and "CalibratedGray" color spaces are regarded as device-independent as they are clearly identified.
Treat ICCBased CMYK as Device CMYK
All embedded ICC profiles that are part of the "DeviceCMYK" color space are removed. This setting prevents unwanted "CMYK" to "CMYK" conversions.
Treat ICCBased RGB and Calibrated RGB as Device RGB
Colors from the "Calibrated RGB and ICCBased RGB" color space are converted to the "Device RGB" color recipe without Color Management. Then the data are converted to the target color space with Color Management and using the set ICC profiles in RGB + "All" or RGB + "Graphic".
Treat ICCBased Gray and Calibrated Gray as Device Gray
Colors from the "Calibrated Gray and ICCBased Gray" color space are converted to the "Device Gray" color recipe without Color Management. The color is used in the K separation. This setting prevents a "chromatic" (CMY) gray.
This is where you can define color matching for each of the listed color spaces.
In addition to selecting ICC profiles, you can set the rendering intent for the individual graphics/image types. Rendering intent determines how color space matching is done. Since losses always occur during a color space transformation, it can be helpful, for example, to retain the photographic perception of an original and to accept a limit on the number of color values. The following parameters are available for rendering intent: "From Document", "Absolute Colorimetric", "Relative Colorimetric", "Saturation" and "Perceptual".
Rendering intent can be treated differently in the following sections:
•CMYK/Gray
•RGB/L*a*b
This color matching is often referred to as gamut mapping and is controlled by the Color Rendering Intent.
Color Rendering Intent is defined in the ICC standard. The following four color matching options are used by the Color Management module and the ICC profiles:
•Absolute Colorimetric
"Absolute Colorimetric" is used for the exact and verifiable reproduction of colors. This Rendering Intent is used for the simulation (proof or proof print) of an output process to another output device or for the output of defined color data in print.
The colors of the original in the color space of the output process are reproduced correctly. All colors that lie outside the color space are mapped to the nearest reproducible color. As a result, very light, very dark or very colorful details in the originals can be lost when they are reproduced. The printing material is simulated during an output process simulation if the lightness and hue of the material lie in the color space of the output process.
•Relative colorimetric
"Relative Colorimetric" is used for the exact and media-dependent reproduction of colors. This Rendering Intent is used for an output process simulation to another output device, where the simulation in part takes into account media white.
The colors of the original are reproduced relative to the white of the media used. The white point of the original is matched to the white point of the reproduction. All colors that lie outside the color space are mapped to the nearest reproducible color. As a result, very dark or very colorful details in the originals can be lost when they are reproduced. The printing material is not simulated during an output process simulation.
•Perceptual
"Perceptual" Rendering Intent is used for the harmonic reproduction of colors in print, taking into account the different color gamuts of the original and print. It is mainly used in the color separation of photographic images.
With this color matching option, the hue in all the natural colors of the original is reproduced for the most part correctly but with restrictions in the contrast. The type of color matching is manufacturer-specific, with the user being able to set some of the aspects such as contrast and chroma change during profile generation.
•Saturation
This Rendering Intent is used whenever the reproduction of chroma in the colors is important in the printed result, while keeping the saturation of the original's color data. It is mainly used in the color separation of graphics and diagrams (business graphics).
With this color matching option, the chroma in all the colors of the original is reproduced as correctly as possible but with restrictions in lightness and hue. The type of color matching is manufacturer-specific, with the user being able to define some settings during profile generation.
•From Document
The Color Rendering Intents that were defined for images and graphics in the PDF file are used.
In gamut mapping, all L shadows that are darker than black ink are matched to black ink and, as a result, shadow definition is lost. This applies especially to "Relative Colorimetric" color matching.
When you check the "Black Point Compensation" option, black point compensation is enabled and matches shadows, consequently preventing a loss of detail.
The "Black Point Compensation" option can be enabled for "Relative Colorimetric" "Perceptual" and "Saturation" color matching.
This is where you select the output profile that describes the properties of the output device you want.
The output profiles can come from different color spaces depending on your output:
•The profile is normally "DeviceCMYK" for printing presses.
•It can be a "DeviceGray" profile for a black-and-white output.
•It can be a "DeviceRGB" profile for a monitor output (e.g. an Internet page).
Use PDF/X Output Intent, if available, as Press Profile
An open PDF/X file with a defined Output Intent and embedded ICC profile is always used as the Press Profile. The set press profile is ignored in this case.
Embed Applied Press Profile as PDF/X Output Intent
The selected press profile is embedded in the PDF file as the PDF/X Output Intent. This can be very useful for comprehensive workflows with the PDF/X format.
Use PDF/X Output Intent, if available, as CMYK Input Profile
An open PDF/X file with a defined Output Intent and embedded ICC profile is used as the source profile for CMYK-to-CMYK conversion. The CMYK profile set in the "Device Colors / DeviceLink" tab is ignored.