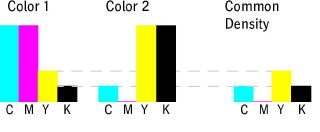
This is the degree to which a color is found in common in each separation of two adjacent colors:

Neutral density simply refers to the lightness/darkness that a color in the overprint leaves behind on the paper.
Each process color (CMYK) has a different ink strength. Neutral density was defined to determine the strength of an ink on paper, with paper white having a neutral density of 0.
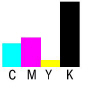
Example of the neutral density for process colors:
|
100% Cyan |
0.61 |
|---|---|
|
100% Magenta |
0.76 |
|
100 % Yellow |
0.16 |
|
100% Black |
1.70 |
The following formula can be used to calculate the "neutral density" in values less than 100%:
|
ND = -1.7 * log (1 - color * (1 - 10 (-0.6 * D) )) |
The neutral density of all separations is calculated from the sum of the neutral densities of the individual separations.