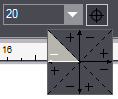
"Select Quadrant"
Angle Control Function "Select Quadrant"
|
|
|
"Select Quadrant" |
This angle control function makes the definition of angles in context-sensitive edit bars much easier for you by automating a part of the angle calculations often needed in the drafting process. It can be accessed via the "Select Quadrant" button found next to each angle edit box. When you click it and hold down the mouse button, the program opens a window with squares (see the examples below), showing you a pseudo-coordinate system divided into 8 parts (the four quadrants, each divided into a plus (+) and a minus (-) zone). Actually, the plus and minus zones apply to the angle zones of the coordinate axes (i.e. the Y axis, when above X, defines the 90° zone; consequently, when you select an adjacent minus zone, the system will subtract the angle of 90° to calculate the actual resulting angle). Hover with the mouse pointer over this window to highlight the quadrant section you want and select it by releasing the left mouse button over it. The default zone is the first quadrant plus.
You can use the "Select Quadrant" angle control function when defining angle attributes of geometric objects (line segments, arcs), layout elements (with the respective "Place part" mode if selected).
Note: Recommendation: It makes sense to use the "Select Quadrant" function whenever the angle in the relevant context-sensitive edit bar is in the range [0° - 90°]. The "Select Quadrant" button is dimmed if the angle box in the context-sensitive edit bar is empty.
Usage
1.Select the appropriate mode and enter the angle you want into the angle box. The "Select Quadrant" angle control function is advisable mainly for angles lying between 0° and 90°.
2.Click the "Select Quadrant" button, and holding down the mouse button drag the mouse pointer over the zone you want in the window with the squares that displays directly below the "Select Quadrant" button:
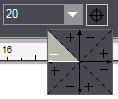
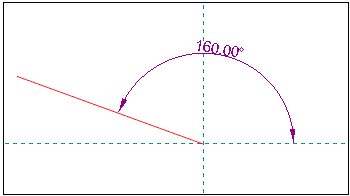
3.Release the mouse button to confirm your selection. The program calculates the actual angle by adding/subtracting the angle currently entered in the context-sensitive edit bar to or from the selected angle zone respectively. In the example above, the program subtracts the current angle of 20° from the selected X coordinate angle zone (180°) to define the actual angle of 160°.
Examples:
Enter an initial value of 20° in the "Angle" box in the context-sensitive edit bar of a regular line. The final value for the angle is 110° (i.e. the angle between the regular line in quadrant 2 and the Y-axis is 20°) after the following quadrant was selected; it is illustrated by the dimension line:
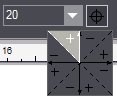
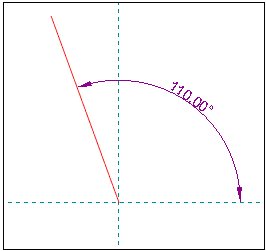
Enter an initial value of 20° in the "Angle" box in the context-sensitive edit bar of a regular line. The final value for the angle is 160° (i.e. the angle between the regular line in quadrant 2 and the X-axis is 20°) after the following quadrant was selected; it is illustrated by the dimension line: