Linearization Files
The optimized printer setting regarding the amount of ink printed on the paper is called linearization. This optimization aims at obtaining a maximum ink density at the lowest possible ink consumption. The linearization result is saved as a separate linearization file (.epl file).
Each linearization file is assigned to a paper profile file and automatically loaded to Color Proof Pro together with the assigned paper profile.
Color Proof Pro differentiates between two linearization types:
Creation of paper profiles and linearization files.
Correction of an existing linearization file.

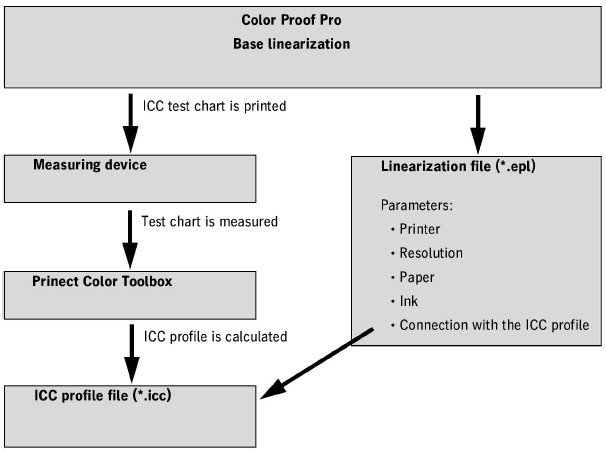
During base linearization, a linearization file (.epl file) is generated. When base linearization is finished, an ICC test chart can be printed. With an appropriate software (such as Heidelberg Prinect Color Toolbox), you can then use this test chart to create a paper profile file (ICC profile).
A linearization file contains details on the proportional amounts of each of the inks that are used when creating the paper profile. The linearization file also contains a reference to the relevant paper profile file. The "Connect Profiles" module is responsible for this (see Connect Profiles). The base linearization determines the physical properties of the interaction between ink and paper and optimizes these properties during profile generation.
The linearization file of a specific color profile automatically loads as well when this color profile is set in Color Proof Pro or a Prinect application that uses Color Proof Pro as the driver. In this way, the properties of the underlying base linearization are set for output, affecting each of the print processes run with this profile.
For information on how to perform a base linearization, please refer to Create Base Linearization
The color reproduction of a printer can vary over time. With a re-linearization, you can readjust the color reproduction of a printer to the state it had when the paper profiles were generated, i.e. during base linearization.
In this way, it is not necessary to generate all paper profiles again if the printer has changed its color application properties over time.
Re-linearization can be performed with a measuring device or by visual judgment. While a measuring device provides exact data, a visual re-linearization is exclusively based on a viewer's judgment and according manual changes.
For information on how to perform a re-linearization, please refer to Re-Linearization by Measurement
When and why is a base or re-linearization necessary?
You must perform a linearization in the following cases:
•Base linearization
A re-linearization should be performed in the following cases:
·Performing a re-linearization at regular intervals ensures that the color reproduction of a printer remains constant. You should re-linearize every two weeks if a printer is used very frequently.
·If only paper profiles are available that were not specifically created for the printer that is to be used. If, for example, existing paper profiles were generated with another printer of the same model, you should re-linearize to match the profiles to the printer in use.
·After a printhead exchange, you should perform a re-linearization.
·An exchange of printer components can change the color properties of the printer.
·You should perform a re-linearization if you notice that the proof prints no longer match older proofs exactly.
Note: Make sure to operate the printer at constant ambient conditions (humidity, temperature, no direct sunlight, etc.). You will obtain stable print results with a linearized device if the above prerequisites are met.